Best Diet for Macular Degeneration: Eye-Healthy Foods That Support Vision
When people talk about a “macular degeneration diet”, they usually mean everyday food choices that may help support overall eye health. This article looks at common nutrients discussed in relation to macular health, examples of foods that contain them, and how they can fit into a balanced eating pattern. It is informational only and not a substitute for medical advice.
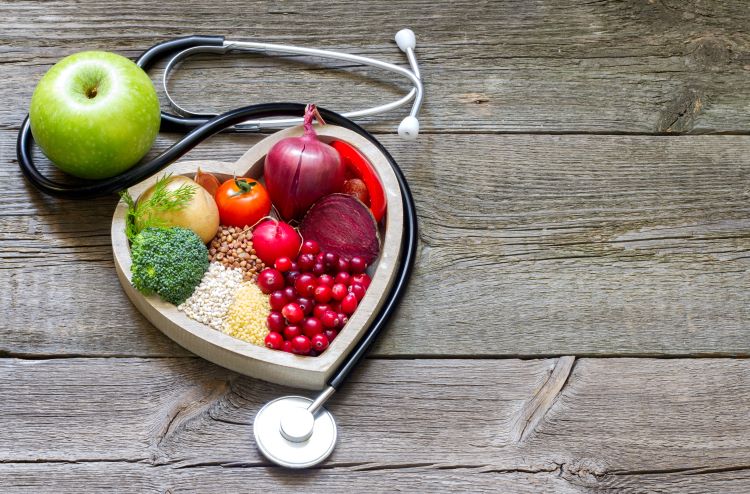

The connection between nutrition and eye health has gained significant attention from researchers and healthcare professionals. The macula, a small but crucial area of the retina, requires specific nutrients to function optimally and resist age-related damage. Poor dietary choices can accelerate oxidative stress and inflammation, contributing to macular degeneration progression.
Why Nutrition Matters for Eye Health
The eyes are constantly exposed to light and oxygen, creating an environment prone to oxidative damage. Free radicals generated by this exposure can harm delicate retinal tissues, particularly the macula. Antioxidants from food help neutralize these harmful molecules, while anti-inflammatory compounds reduce chronic inflammation that contributes to eye disease. Studies have shown that people consuming diets rich in specific nutrients have lower rates of macular degeneration and slower disease progression when it does occur.
Key Nutrients for a Healthy Macula
Several nutrients play critical roles in maintaining macular health. Lutein and zeaxanthin, known as macular pigments, filter harmful blue light and act as natural sunglasses for the retina. Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA, support retinal structure and reduce inflammation. Vitamins C and E provide powerful antioxidant protection, while zinc helps transport vitamin A to the retina and supports overall eye function. Beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A, is essential for night vision and overall retinal health.
Foods for Macular Degeneration
Leafy green vegetables like spinach, kale, and collard greens contain the highest concentrations of lutein and zeaxanthin. These should form the foundation of an eye-healthy diet. Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines provide essential omega-3 fatty acids. Colorful fruits and vegetables, including carrots, sweet potatoes, bell peppers, and berries, offer various antioxidants and vitamins. Nuts and seeds, particularly almonds and sunflower seeds, contribute vitamin E and healthy fats. Eggs contain lutein, zeaxanthin, and zinc in easily absorbed forms.
Simple Eating and Lifestyle Tips
Incorporating eye-healthy foods into daily meals doesn’t require dramatic dietary changes. Start by adding a handful of leafy greens to smoothies, sandwiches, or salads. Choose colorful vegetables and fruits at each meal to ensure a variety of nutrients. Replace processed snacks with nuts or seeds. Cook with olive oil instead of butter to increase healthy fat intake. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of refined carbohydrates, which can promote inflammation. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Building a Long-Term Eye-Healthy Lifestyle
Sustaining dietary changes requires planning and gradual implementation. Meal preparation can help ensure eye-healthy foods are readily available. Growing a small herb or vegetable garden provides fresh, nutrient-dense produce. Reading nutrition labels helps identify foods high in beneficial nutrients while avoiding those with excessive sugar or unhealthy fats. Regular eye exams remain crucial for monitoring macular health, even with optimal nutrition. Combining proper diet with other lifestyle factors like wearing sunglasses, not smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight maximizes protective benefits.
Nutrition plays a vital role in supporting macular health and potentially slowing the progression of age-related macular degeneration. While dietary changes cannot cure the condition, consuming foods rich in lutein, zeaxanthin, omega-3 fatty acids, and other essential nutrients provides the eyes with tools to fight oxidative damage and inflammation. Building sustainable eating habits that include plenty of leafy greens, colorful fruits and vegetables, fatty fish, and nuts creates a foundation for long-term eye health. Combined with regular eye care and healthy lifestyle choices, proper nutrition offers a practical approach to preserving vision and maintaining quality of life.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.